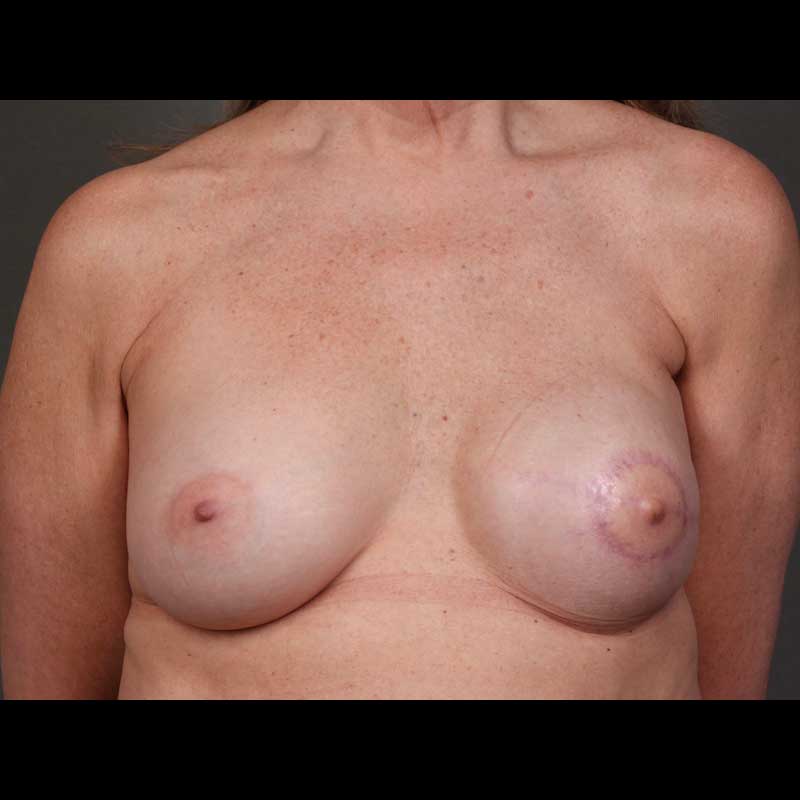
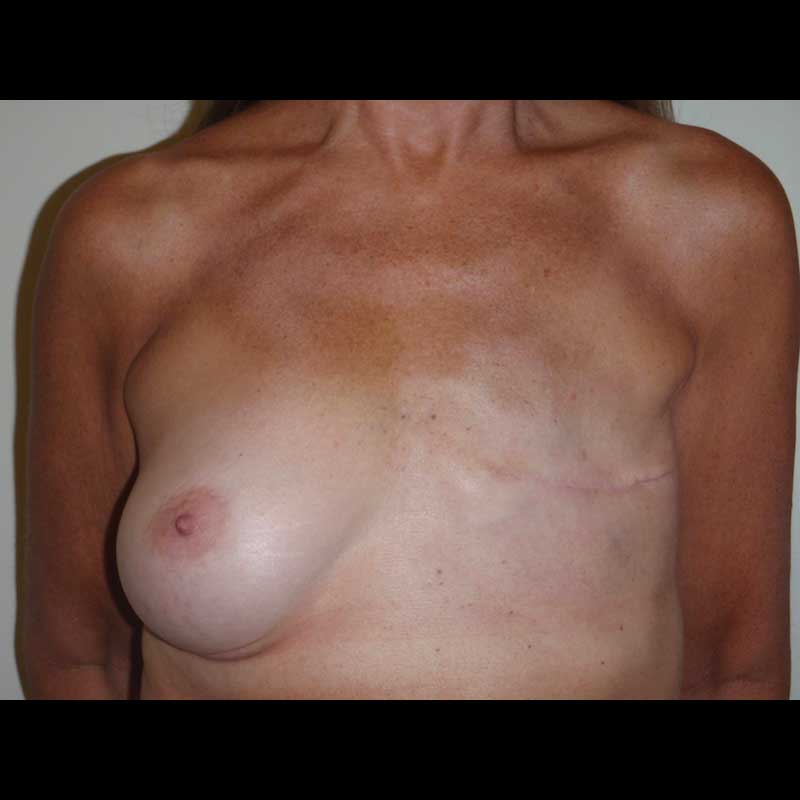
Summary
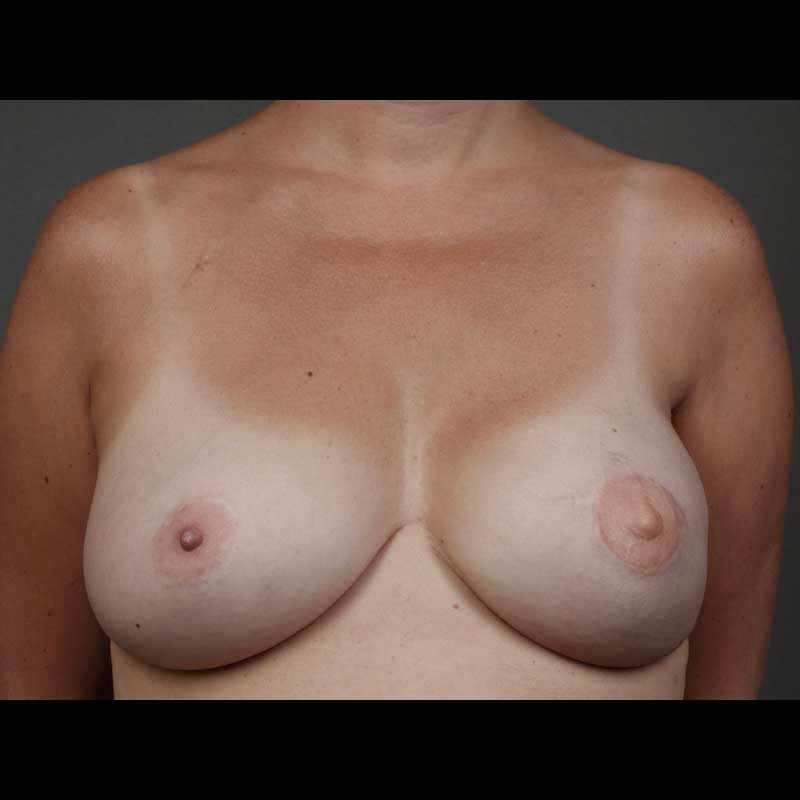
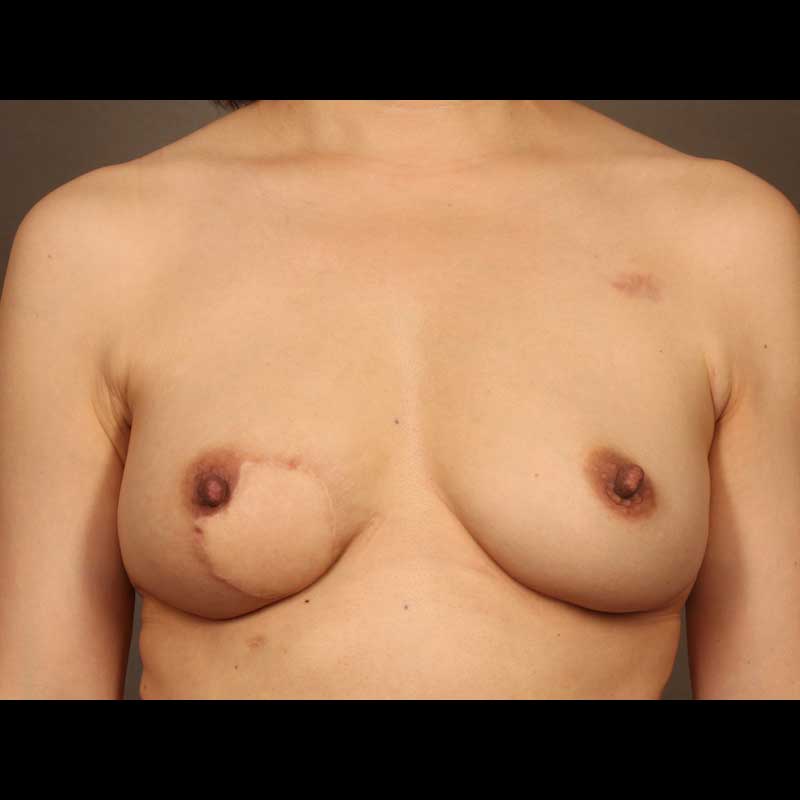
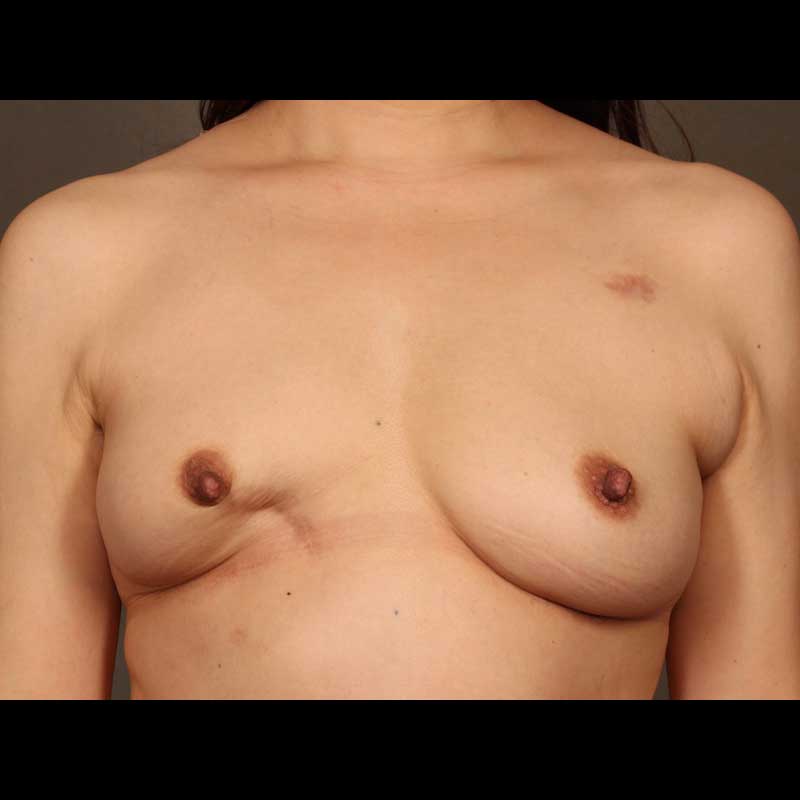
Implant reconstruction generally requires more than one operation to reach a final breast shape. Breast revision procedures following implant reconstruction are typically outpatient procedures. While the healed mastectomy scar can be used for revision surgery in many cases, sometimes new incisions are needed to achieve optimal breast contour. In some cases, secondary breast revision can also be done at the time of nipple areola reconstruction.
While direct-to-implant or “one-step” breast reconstruction with an implant avoids the use of a tissue expander, some patients still choose to have secondary revision procedures to maximize the quality of their breast reconstruction.
Types of procedures
- Capsular contracture surgery: A capsule is the normal internal layer of scar tissue that occurs around a breast implant. While the capsule does not typically cause problems, if the capsule scar tissue contracts, it can cause uncomfortable tightness and may even be visible. Revision surgery can release or remove an abnormal capsule to alleviate tightness and help create a softer breast reconstruction.
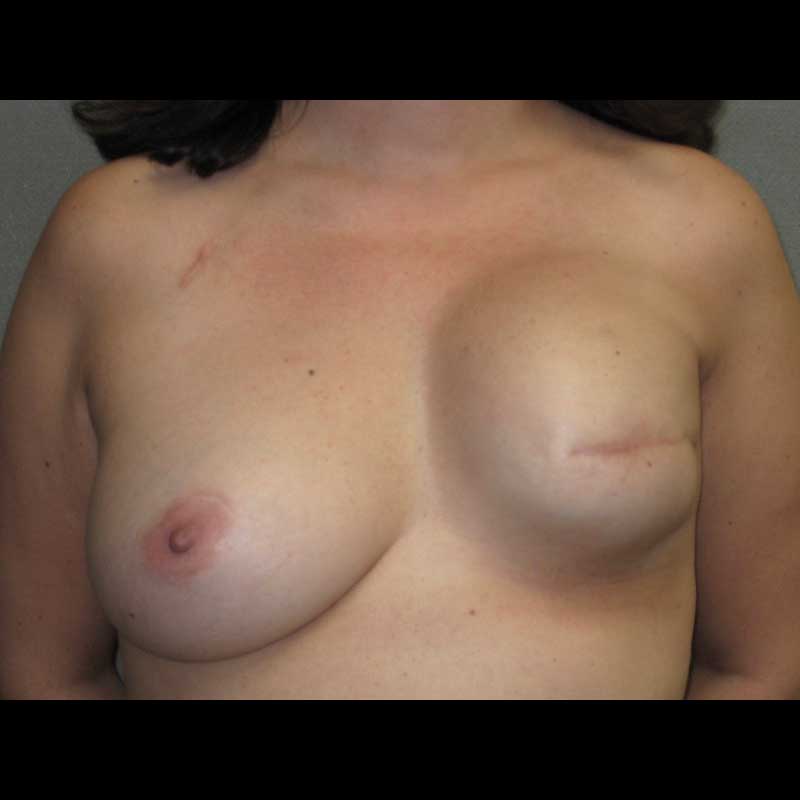
- Contour or symmetry corrective surgery: Undesirable breast contour can be corrected by reshaping the skin envelope around the breast or through fat grafting using fat harvested with liposuction. Surgery on the opposite breast can also help correct breast asymmetry.
- Acellular dermal matrix placement: Revision surgery using an acellular dermal matrix, frequently improves issues related to implant malposition, capsular contracture, skin rippling, and thin skin. When an implant capsule is repaired or removed in order to help improve implant positioning, the acellular dermal matrix may help to reinforce the capsule or thin skin that might otherwise reveal visible implant irregularities.
- Prepectoral conversion: Some women with subpectoral breast implants have visible or uncomfortable animation of their implants. This type of deformity can be corrected by moving the breast implants from a subpectoral position under the muscle to a prepectoral position over the muscle.
Procedure details
- Typically performed on an out-patient basis
- Our surgeons can help you determine which revision procedures best suit your unique situation
- Revision surgery can be done to change the type of implant, correct the surrounding capsule, or alter the overlying soft tissue
- In some cases, nipple reconstruction may be done at the same time
- Revisions can be performed in the months after the initial reconstruction or may be done years later if desired
Risks & Benefits
Risks related to implant revision surgery depend on the procedure being done. The risks are generally limited, since revision surgery is done once the breast reconstruction has fully healed and not at the same time as the mastectomy.
Revision procedures are typically done as outpatient surgical procedures with recoveries that are much easier than the original mastectomy and reconstruction surgery. If you are unhappy with your implant breast reconstruction, the surgeons at NYBRA Plastic Surgery can help you understand your options.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many years after implant breast reconstruction do I need to change my implants?
There is no predetermined time after which you need to change your breast implants. This is true whether you have saline filled implants or silicone gel filled implants. If you are comfortable with your implants, and you are not having any problems with your breast reconstruction, you do not need to change your implants.
If I want to have surgery to improve my implant breast reconstruction, will my insurance company consider this to be cosmetic surgery?
Insurance coverage for any breast surgery for patients with breast cancer or after mastectomy (for patients with or without breast cancer) is mandated by federal guidelines as described in The Women’s Health and Cancer Rights Act of 1998. Insurance is compelled cover breast revision surgery regardless of how long it is done after the original reconstructive surgery.